Space & Astronomy
13 min read
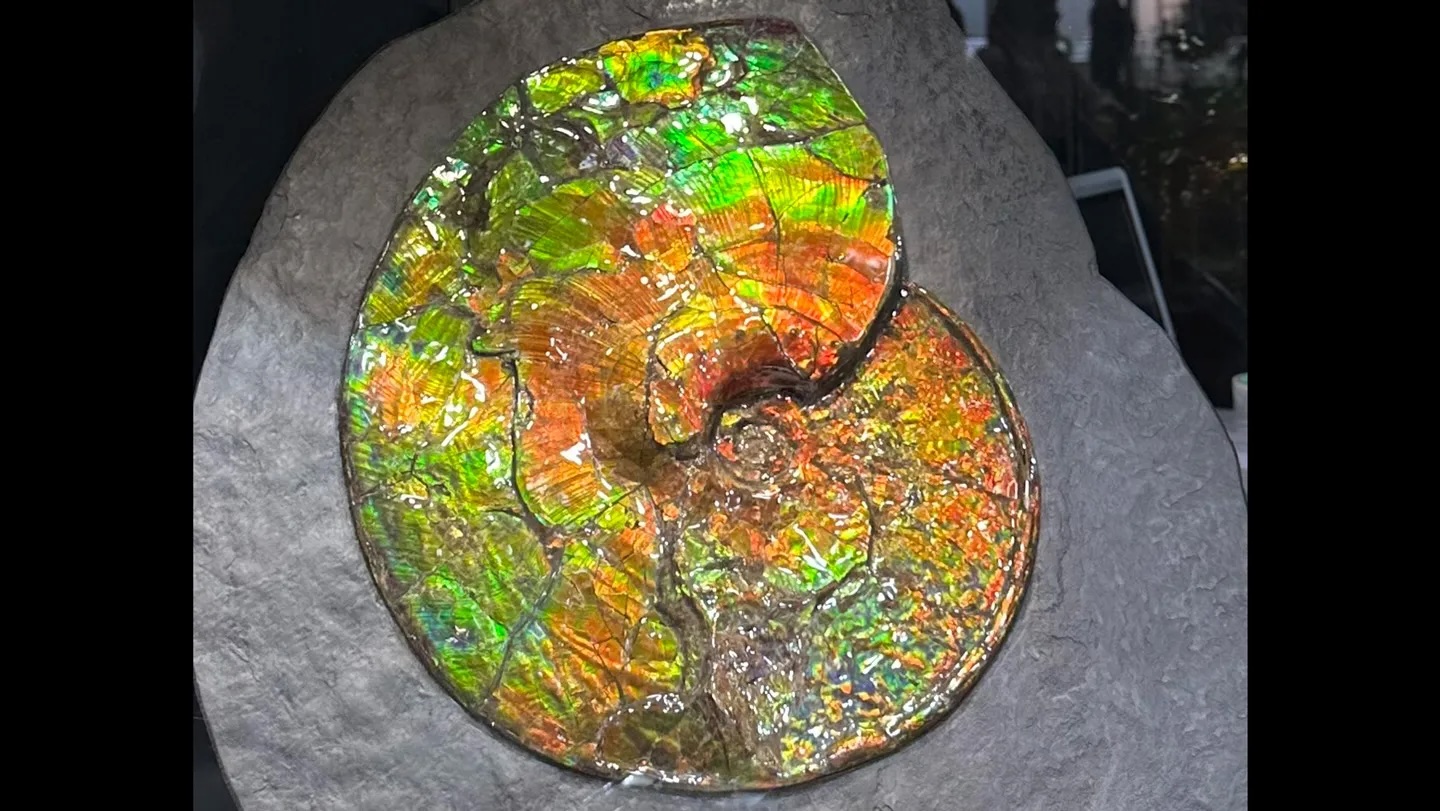
Unveiling the Rainbow Shimmer of Ammolite Gems
Science News Explores
January 20, 2026•2 days ago
AI-Generated SummaryAuto-generated
Ammolite gems, derived from fossilized ammonite shells, exhibit a rainbow shimmer due to structural color. This iridescence arises from the microscopic layers of aragonite, a mineral found in the shells. The arrangement of these layers causes light to refract and reflect, creating the vibrant, shifting hues. This phenomenon is similar to how colors appear on butterfly wings or peacock feathers.
ammonites: A group of extinct cephalopods known as ammonoids. Distantly related to squids and octopuses, these sea creatures lived from about 415 million years ago until the end of the Age of Dinosaurs, roughly 66 million years ago. Ammonites had a flat, spiral shell that sort of resembled a coiled snake. Their shells’ interior was divided into a series of chambers. Today, their fossil remains are often prized as art of for use in jewelry.
ammolites: A semi-precious gem derived from the fossil shells of certain ammonites, extinct cephalopods known as ammonoids that died out 66 million years ago (and were distantly related to squids and octopuses).
colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
electron microscope: A microscope with high resolution and magnification that uses electrons rather than light to image an object.
extinct: (n. extinction) An adjective that describes a species for which there are no living members.
fossil: Any preserved remains or traces of ancient life. There are many different types of fossils: The bones and other body parts of dinosaurs are called “body fossils.” Things like footprints are called “trace fossils.” Even specimens of dinosaur poop are fossils. The process of forming fossils is called fossilization.
hue: A color or shade of some color.
Madagascar: This island nation sits in the Indian Ocean, just east of the African nation of Mozambique.
materials scientist: A researcher who studies how the atomic and molecular structure of a material is related to its overall properties. Materials scientists can design new materials or analyze existing ones. Their analyses of a material’s overall properties (such as density, strength and melting point) can help engineers and other researchers select materials that are best suited to a new application.
microscope: An instrument used to view objects — such as bacteria or the single cells of plants or animals — that are too small to be visible to the unaided eye.
mineral: Crystal-forming substances that make up rock, such as quartz, apatite or various carbonates. Most rocks contain several different minerals mish-mashed together. A mineral usually is solid and stable at room temperatures and has a specific formula, or recipe (with atoms occurring in certain proportions) and a specific crystalline structure (meaning that its atoms are organized in regular three-dimensional patterns).
model: A simulation of a real-world event (usually using a computer) that has been developed to predict one or more likely outcomes. Or an individual that is meant to display how something would work in or look on others.
nacre: Also known as mother-of-pearl, this is the hard, pearly, iridescent coating on the inner surface of a mollusk’s shell.
nautilus: A type of cephalopod found in the South Pacific and Indian oceans and that has a spiral-shaped shell filled with chambers.
organic: (in chemistry) An adjective that indicates something is carbon-containing; also a term that relates to the basic chemicals that make up living organisms.
rainbow: An arc of color displayed across the sky during or just after a rain. It’s caused when water droplets in the atmosphere bend (or diffract) white sunlight into a number of its component hues: usually red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
recall: To remember.
shell: The normally hard, protective outer covering of something. It could cover a mollusk or crustacean (such as a mussel or crab), a bird’s egg or some other relatively soft tissue that needs protection (such as a tree nut or peanut).
silica: A mineral, also known as silicon dioxide, containing silicon and oxygen atoms. It is a basic building block of much of the rocky material on Earth and of some construction materials, including glass.
species: A group of similar organisms capable of producing offspring that can survive and reproduce.
structural color: A color caused by the structural shape of some object not by a pigmented molecule. Examples include the blues on some bird feathers and butterfly wings that are not pigmented; they just reflect light in such a way that their material appears deep blue.
Rate this article
Login to rate this article
Comments
Please login to comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
